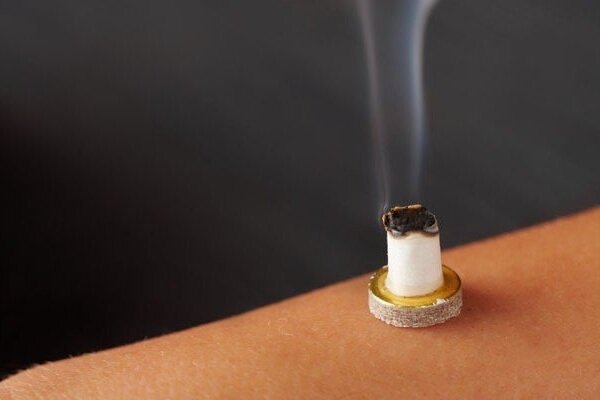


Moxibustion
Moxibustion is the process where moxa sticks, made of dry moxa leaves (Artemisia vulgaris) is ignited and held about an inch above the patients’s skin over specific acupuncture points. Moxa is available in a loose form that can be used for making moxa cones. Alternatively, moxa is packed and rolled in a long stick like a large cigar, about 15-20 cm long and about 1-2 cm in diameter. The purpose of this process is to warm the Qi and blood in the channels. Moxibustion is most commonly used when there is the requirement to expel cold and damp or to tonify the Qi and blood. A single treatment of moxibustion usually lasts 10-15 minutes. Needle-warming moxibustion combines needling and moxibustion by attaching a moxa stub (about 2 cm long) to an inserted needle. This method enhances the effects of needling and is often used to treat chronic rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis.
Citing: College of Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioners and Acupuncturists of British Columbia. (2016). What is Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Retrieved from https://www.ctcma.bc.ca/public-protection/what-is-tcm
MOXIBUSTION (DDEUM, 灸)
Moxibustion (Ddeum) is one of Traditional Oriental Medicine treatment modalities. Dried Ssuk (aka. moxa) is burnt on (or over) acupuncture points and particular locations of the body. The heat from burning Ssuk warms up the channels and collaterals in the body, and promotes the smooth circulation of Qi and blood. Furthermore, moxibustion ultimately helps restore vitality and balance the body’s physiological functions. Moxibustion can be performed directly or indirectly on the skin with Ssuk wool, Ssuk cones and sticks, and on needles as ‘warm needle technique’.
Moxibustion has great effect on all the Cold syndromes, and is highly recommended to those in chronic and deficiency conditions. It also helps promote cell tissue functions, improve immune system, and increase hemoglobin. Often along with acupuncture treatment, moxibustion is commonly used in clinic to treat hypertension, arteriosclerosis, anemia, gastric ulcer, hives and more.
MOXA (SSUK; Ai Ye 艾葉 in TCM)
Moxa (Ssuk, Korean wormwood, Korean mugwort; Artemisia princepts Pamp.) is an Asian plant in chrysanthemum species, native to Korea, China, Japan and Europe.
In A New Compilation of Materia Matica appears the following description: “The medicinal ssuk is bitter and pungent in taste. Its nature is warm in raw and hot in cooked. Ssuk brings up the severed Yang, circulates 12 Channels, runs 3 Yin, benefits Qi & blood, and warms the uterus… … Therefore, when burned, the hot energy of ddeum ssuk (moxa prepared for Moxibustion therapy) penetrates all the Channels and Collaterals to eliminate hundreds of diseases.”
“艾葉苦辛 生溫 熟熱 純陽之性 能回垂絶之陽 通十二經 走三陰 理氣血 逐寒濕 暖子宮… … 以之灸火 能透諸 經而除百病” [本草叢新]
Ssuk (Moxa) for its warm nature can activate Yang. Its pungent odour can travel through the Channels, regulate Qi and blood, and expel Cold from the Channels, and its bitter nature resolves Dampness. Ddeum ssuk, as prepared by micro-grinding up to a fragrant fluff, easily burns down to warm the skin and penetrate deeper, carrying its heat energy into the core of the body without damaging skin tissues. As a result it is best used as a necessary material in Moxibustion treatment.